Obesity is a widespread concern in today’s society, impacting millions of individuals worldwide. With its detrimental effects on physical and mental well-being, understanding the health risks associated with obesity is crucial. From increased risks of chronic diseases to decreased quality of life, this article explores the various health risks that obesity can pose, shedding light on the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for overall wellness.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
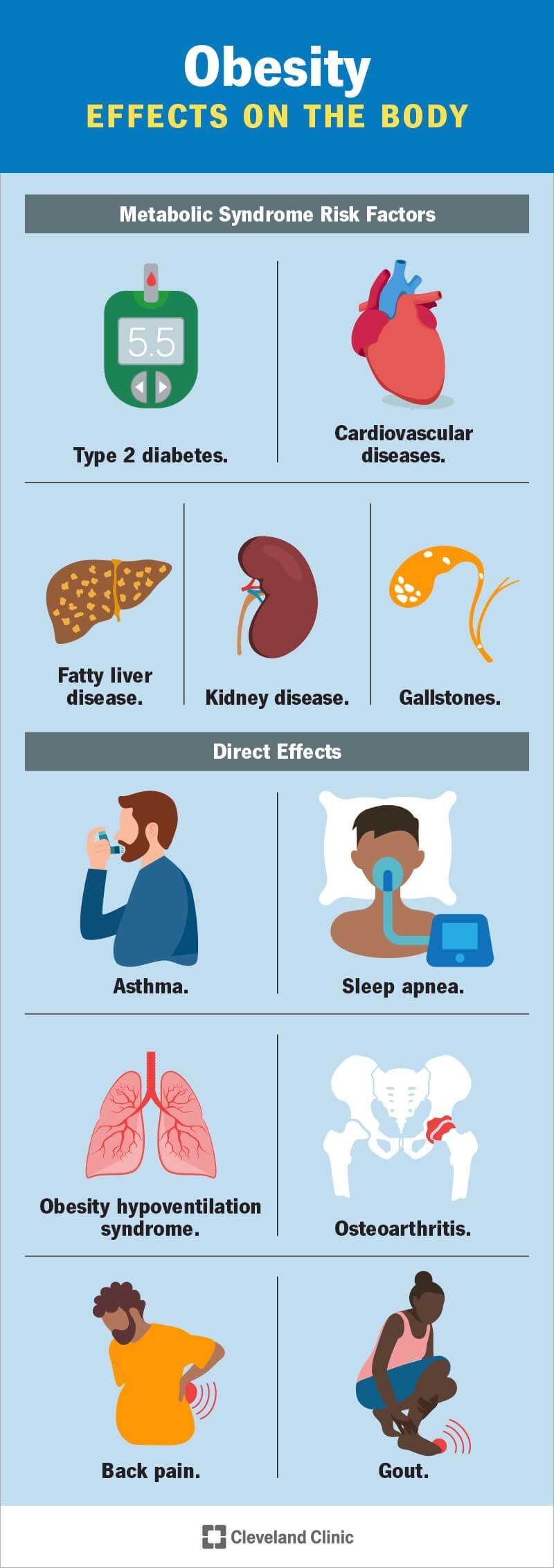
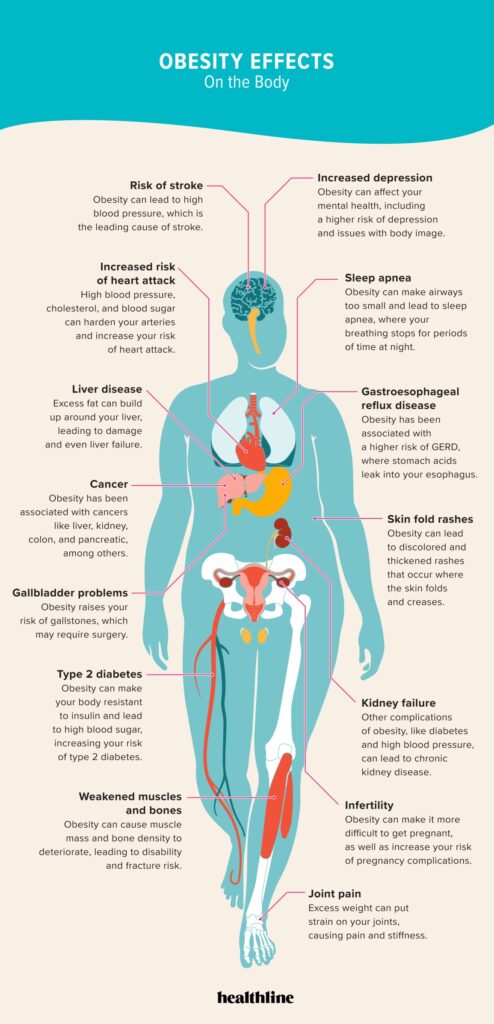
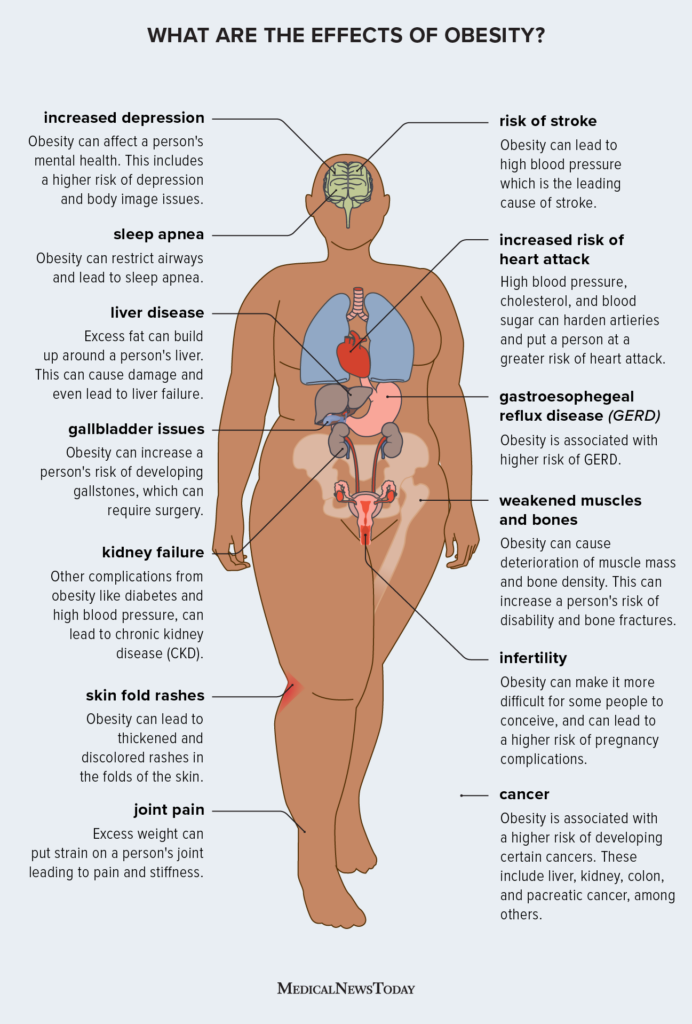
Heart Disease
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects many individuals who are obese. When you carry excess weight, your heart has to work harder to pump blood throughout your body, leading to an increase in blood pressure. This can put a strain on your arteries and lead to various cardiovascular complications. It is essential to manage your blood pressure levels to reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrow or blocked due to the accumulation of plaque. Obesity is a significant risk factor for this condition since excess body fat can lead to an increase in cholesterol levels and inflammation, which contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries. This condition can result in chest pain, heart attacks, and even heart failure if left untreated.
Heart Attack
Obesity significantly increases the risk of experiencing a heart attack. The excessive fat in your body can lead to an imbalance in cholesterol levels and trigger the formation of blood clots, which can block the blood flow to your heart. This lack of blood flow can cause a heart attack, leading to severe damage to your heart muscle. It is crucial to maintain a healthy weight to reduce the chances of experiencing such a life-threatening event.
Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Obesity is closely linked to insulin resistance, as excess fat hinders the body’s ability to use insulin efficiently. This resistance causes blood sugar levels to rise, leading to the development of type 2 diabetes. It is essential to manage your weight to reduce the risk of developing this chronic condition.
High Blood Sugar
Obesity significantly increases the risk of high blood sugar levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia. When your body has an excessive amount of fat, it becomes difficult for insulin to transport glucose from your blood into the cells, causing glucose to accumulate in the bloodstream. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including nerve damage, cardiovascular problems, and kidney disease.
Pancreatic Damage
Obesity can cause damage to the pancreas, the organ responsible for producing insulin. Excess fat in the body contributes to inflammation, which can impair pancreatic function. This damage can further worsen insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in preserving the health and function of your pancreas.
Stroke
Reduced Blood Flow to the Brain
Obesity increases the risk of reduced blood flow to the brain and consequently raises the likelihood of suffering a stroke. Excess weight can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the brain. This reduced blood flow can result in a stroke, which may cause permanent brain damage or even prove fatal.
Blood Clots
Obesity is a significant risk factor for the formation of blood clots, a dangerous condition known as thrombosis. Excess body fat contributes to an increase in blood clotting factors, which can lead to the development of blood clots. These clots can travel to the brain, blocking vital blood vessels and causing a stroke. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in reducing the risk of blood clot formation.
Brain Hemorrhage
Obesity increases the risk of a brain hemorrhage, a condition characterized by bleeding within the brain. The excessive weight can strain blood vessels, making them more susceptible to rupture and causing bleeding into the brain tissue. This condition can lead to severe neurological complications and, in some cases, prove fatal. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in minimizing the risk of experiencing a brain hemorrhage.
Cancer
Breast Cancer
Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, particularly in postmenopausal women. The accumulation of excess fat in the body can lead to an increase in estrogen levels, which can contribute to the development of breast cancer. Additionally, obesity is linked to chronic inflammation, which also plays a role in cancer formation. Maintaining a healthy weight and incorporating regular physical activity are essential in reducing the risk of breast cancer.
Colorectal Cancer
Obesity is a known risk factor for colorectal cancer, which affects the colon or rectum. Studies have shown that individuals who are obese have a higher likelihood of developing this type of cancer. The exact reasons behind this correlation are not fully understood, but it is believed that the inflammation caused by excess body fat and the changes in hormone levels play a role. A healthy weight and a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help lower the risk of colorectal cancer.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer refers to cancer that develops in the lining of the uterus, and obesity is a significant risk factor for this disease. The excess fat in the body causes an increase in estrogen levels, which can promote the growth of abnormal cells in the endometrium. This increased cell growth can lead to the development of endometrial cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in reducing the risk of this type of cancer.
This image is property of medlineplus.gov.
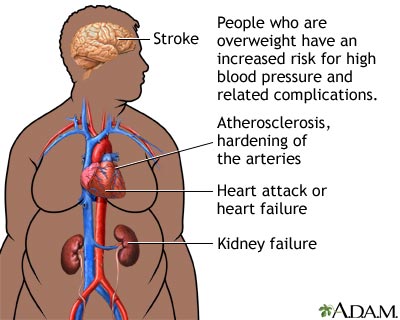
Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obesity is closely linked to obstructive sleep apnea, a sleep disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep. Excess fat around the neck and throat can cause the airway to become blocked, leading to disturbances in breathing. This condition can result in frequent awakenings during the night, daytime fatigue, and other health complications. Managing and reducing obesity is essential in improving sleep quality and reducing the impact of sleep apnea.
Daytime Fatigue
Sleep apnea, commonly associated with obesity, can lead to excessive daytime fatigue. The interruptions in breathing during sleep prevent individuals from obtaining a restful night’s sleep, leaving them feeling tired and fatigued during the day. This fatigue can affect daily activities, productivity, and overall quality of life. By maintaining a healthy weight and addressing sleep apnea, individuals can reduce daytime fatigue and improve their overall well-being.
Increased Risk of Accidents
The combination of obesity and sleep apnea significantly increases the risk of accidents. Excessive daytime fatigue caused by sleep apnea can impair cognitive function, reflexes, and concentration, making individuals more susceptible to accidents while driving or operating machinery. Addressing obesity and managing sleep apnea are crucial steps in ensuring the safety of both individuals and those around them.
Joint Problems
Osteoarthritis
Obesity is a major risk factor for developing osteoarthritis, a joint disorder characterized by the breakdown of cartilage. The excess weight places additional stress on the joints, particularly in weight-bearing areas such as the knees and hips. Over time, this increased stress can lead to the deterioration of cartilage and cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in reducing the strain on joints and preventing the onset of osteoarthritis.
Increased Stress on Joints
Excess body weight places increased stress on the joints, which can lead to various joint problems. The additional strain affects the cartilage and can contribute to the development of conditions such as osteoarthritis or joint injuries. It is crucial to maintain a healthy weight to minimize the stress on joints and prevent the onset of these painful and debilitating conditions.
Limited Mobility
Obesity can significantly impact mobility due to joint problems and decreased flexibility. The excess weight places strain on joints, making movement more difficult and painful. This limited mobility can hinder daily activities, reduce quality of life, and further contribute to weight gain. By managing and reducing obesity, individuals can improve their mobility, regain functionality, and enhance their overall well-being.

This image is property of assets.lybrate.com.
Gallbladder Disease
Gallstones
Obesity is a significant risk factor for gallstones, which are solid deposits that form in the gallbladder. The excess body weight can lead to an imbalance in bile composition, causing the formation of gallstones. These stones can obstruct the bile ducts, leading to severe pain, inflammation, and other complications. Maintaining a healthy weight and following a balanced diet can reduce the risk of gallstone formation and gallbladder disease.
Inflammation
Obesity contributes to chronic inflammation, which can affect various organs, including the gallbladder. Inflammation in the gallbladder can disrupt its function and contribute to the development of gallbladder disease. It is crucial to manage obesity to reduce inflammation levels and support optimal gallbladder health.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, is often associated with obesity. The excessive fat in the body can contribute to the development of gallstones, which can lead to inflammation and infection within the gallbladder. Cholecystitis can cause severe pain, digestive issues, and other complications. By maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can lower the risk of cholecystitis and promote a healthy gallbladder.
Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Obesity is closely linked to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. Excess body weight can lead to the buildup of fat in the liver cells, impairing their function and causing inflammation. NAFLD can progress to more severe conditions, such as liver fibrosis or cirrhosis, if left untreated. Managing obesity and adopting a healthy lifestyle are crucial in reducing the risk of NAFLD and promoting liver health.
Liver Inflammation
The excessive fat present in the body due to obesity can lead to liver inflammation. Inflammation in the liver can hinder its normal function and contribute to various liver diseases. The inflammatory response can further exacerbate the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to a vicious cycle of inflammation and liver damage. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in preventing liver inflammation and preserving liver health.
Liver Failure
Obesity increases the risk of liver failure, a life-threatening condition in which the liver loses its ability to function properly. The accumulation of fat in the liver due to obesity can lead to progressive liver damage, which can eventually result in liver failure. This condition can have severe consequences, necessitating a liver transplant for survival. By managing obesity, individuals can reduce the risk of liver failure and maintain the health of their liver.
This image is property of post.medicalnewstoday.com.
Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease
Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The excess weight places a strain on the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function over time. Obesity-related conditions, such as high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, also contribute to the development of CKD. This chronic condition can result in kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Managing obesity and adopting a healthy lifestyle are crucial in reducing the risk of CKD and preserving kidney health.
Kidney Failure
Obesity increases the risk of kidney failure, a condition in which the kidneys can no longer function adequately to maintain vital bodily functions. The excess weight places stress on the kidneys, leading to a decline in their function over time. Kidney failure can have severe consequences, necessitating dialysis or a kidney transplant for survival. By managing obesity, individuals can lower the risk of kidney failure and promote the health of their kidneys.
Proteinuria
Proteinuria refers to the presence of excess protein in the urine, and obesity is a significant risk factor for this condition. When the kidneys are damaged due to obesity-related factors, they may not effectively filter waste products and proteins from the blood. This can result in proteinuria, which can further progress to more severe kidney conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in reducing the risk of proteinuria and protecting kidney function.
Pregnancy Complications
Gestational Diabetes
Obesity increases the risk of gestational diabetes, a form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. Excess body fat can impair the body’s ability to use insulin efficiently, leading to high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. This condition can pose risks to both the mother and the baby, including an increased likelihood of requiring a cesarean delivery and the potential development of type 2 diabetes in the future. By managing obesity before and during pregnancy, the risk of gestational diabetes can be reduced.
High Blood Pressure
Obesity raises the risk of high blood pressure during pregnancy, a condition known as gestational hypertension. The excessive weight places added strain on the circulatory system, leading to increased blood pressure levels. This condition can result in complications such as preeclampsia, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. Managing obesity and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial in reducing the risk of high blood pressure during pregnancy.
Premature Birth
Obesity is associated with an increased risk of premature birth, delivering the baby before the completion of the full term of pregnancy. Premature birth can pose various health risks to the baby, including respiratory issues, developmental delays, and other complications. By managing obesity before and during pregnancy, the risk of premature birth can be reduced, promoting the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
In conclusion, obesity poses significant health risks across various body systems and can lead to severe, life-threatening conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and overall lifestyle management is crucial in reducing the risks associated with obesity. By understanding and addressing these risks, we can take proactive steps towards a healthier and happier life. Remember, your health matters, and it’s never too late to make positive changes.
This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.