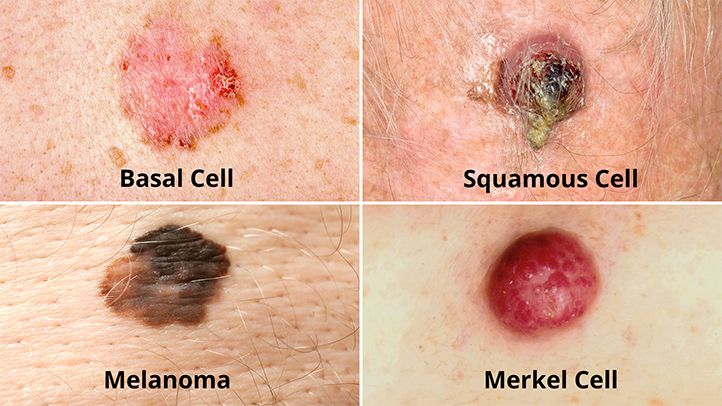
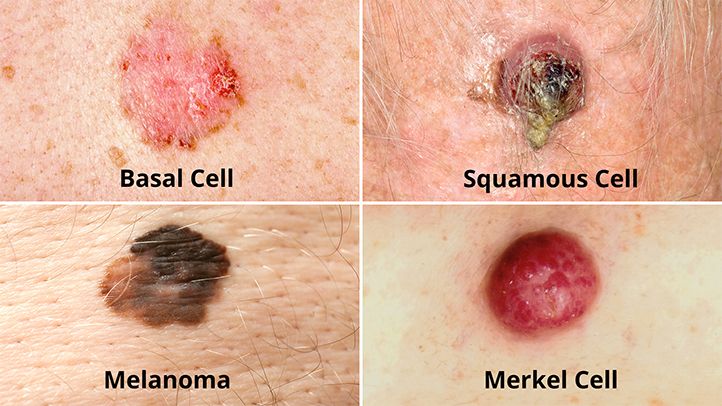
Skin cancer is a serious health concern that affects many people worldwide. It is important to be aware of the early signs of skin cancer in order to detect it early and seek proper treatment. Understanding the warning signs such as changes in moles, new growths, or unusual skin discolorations, can make a significant difference in preventing the cancer from spreading. By staying vigilant and seeking medical attention at the first sign of abnormalities, you can protect yourself against the potential dangers of skin cancer. Skin cancer is a serious health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. Recognizing the early signs of skin cancer is crucial for early detection and successful treatment. In this article, we will explore the common types of skin cancer, the risk factors associated with its development, prevention methods, and the specific signs to look out for in each type of skin cancer.
This image is property of miiskin.com.
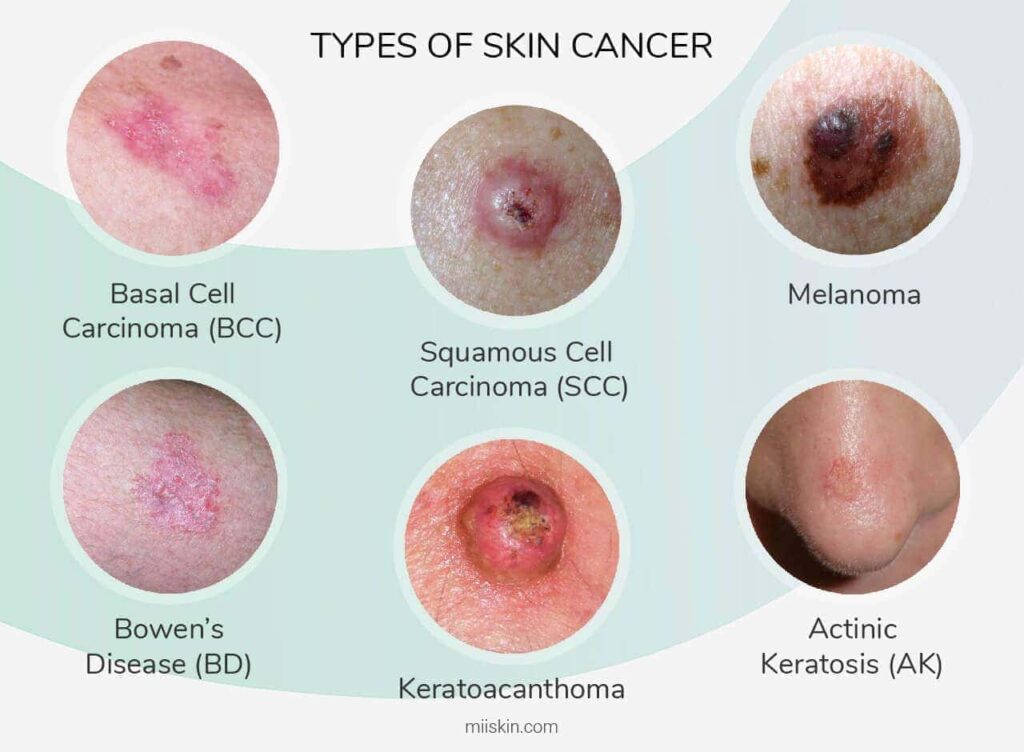
Common Types of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of all cases. It often appears as a raised, pearly bump on the skin, which may develop into an open sore that crusts and bleeds. BCC typically occurs on sun-exposed areas, such as the face and neck, and is slow-growing.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a rough, scaly patch or a rapidly growing bump with a crusted surface. SCC can occur on any sun-exposed area, including the face, hands, and ears. If left untreated, SCC can become invasive and potentially spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most aggressive and deadliest form of skin cancer. It originates from the cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for giving color to the skin, hair, and eyes. Melanoma can develop from existing moles or appear as new growths on the skin. It is essential to detect melanoma early, as it can spread rapidly to other organs and tissues.
Risk Factors
Various risk factors increase the likelihood of developing skin cancer. By understanding these factors, you can take proactive steps to minimize your risk. Some common risk factors include:
Excessive exposure to UV radiation
Repeated exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds increases the risk of developing skin cancer.
Fair skin complexion
People with fair skin, freckles, light hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible to skin damage from UV radiation.
Family history of skin cancer
If you have a close relative who has had skin cancer, your risk of developing the disease may be higher.
Weakened immune system
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as transplant recipients or those with certain medical conditions, have an increased risk of developing skin cancer.
History of excessive sunburns
A history of severe sunburns, particularly during childhood, can elevate the risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation
Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic, or radiation, such as therapeutic radiation treatments, can contribute to the development of skin cancer.
Presence of moles or atypical moles
Having numerous moles or atypical moles (dysplastic nevi) on your skin can increase the risk of melanoma.
Age
As individuals get older, their risk of skin cancer increases. However, skin cancer can occur at any age.
Gender
Men are more likely than women to develop skin cancer, particularly melanoma.
Skin Cancer Prevention
Prevention is key when it comes to reducing the risk of skin cancer. By incorporating these preventive measures into your lifestyle, you can protect your skin and minimize the chances of developing skin cancer:
Sun protection measures
Wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts, and seeking shade during peak sun hours (usually between 10 am and 4 pm) can help reduce exposure to harmful UV radiation.
Avoiding tanning beds
Tanning beds emit UV radiation, similar to the sun, and can significantly increase the risk of skin cancer. It is best to avoid them altogether.
Regularly examining your skin
Performing regular self-examinations of your skin can help identify any changes or new moles that may be a cause for concern. If you notice anything suspicious, consult a dermatologist.
Using sunscreen
Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF (sun protection factor) of 30 or higher to any exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
Avoiding peak sun hours
Try to limit your time spent outdoors during the peak sun hours when the sun’s rays are strongest.
Avoiding UV radiation exposure from other sources
Protect your skin from other sources of UV radiation, such as tanning lamps and booths, by avoiding them altogether.
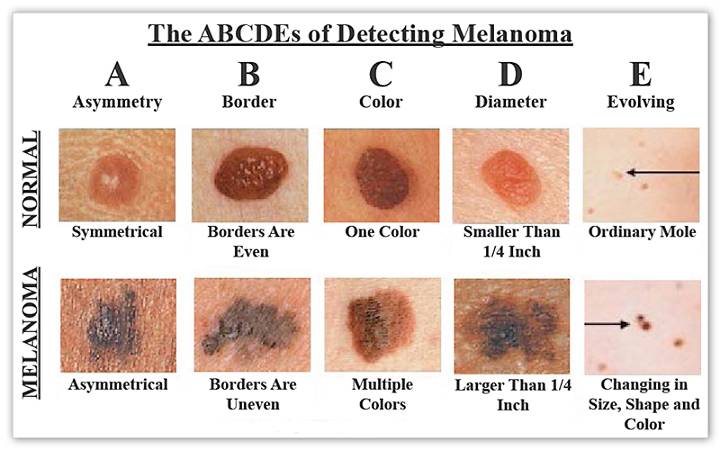
Early Signs of Skin Cancer
Detecting skin cancer early greatly improves the chances of successful treatment. Keep an eye out for the following early signs:
Changes in existing moles
If you notice any changes in size, shape, color, or texture of an existing mole, it may be a warning sign of skin cancer.
New moles or growths
The development of new moles or growths on your skin, especially after the age of 30, should be monitored closely.
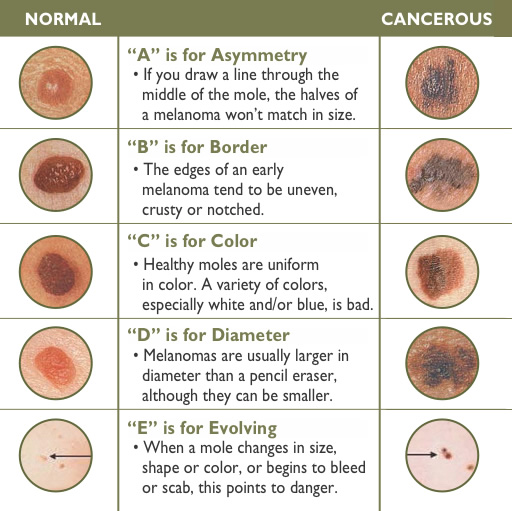
Moles with irregular borders
Moles with jagged, scalloped, or blurred borders are a potential sign of skin cancer.
Moles with uneven coloration
Moles that have varying shades of brown, black, white, red, or blue within them may require further evaluation.
Moles that are asymmetrical
If a mole is asymmetrical, meaning one half does not match the other half in terms of shape or size, it should be examined by a dermatologist.
Moles larger than 6 millimeters
Moles larger than the size of a pencil eraser should be assessed for potential malignancy.
Moles that itch, bleed, or crust
Any mole that becomes itchy, bleeds, or forms a crust should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Persistent sores that don’t heal
Non-healing sores or ulcers on the skin that persist for weeks can be a sign of skin cancer.
Red or inflamed patches of skin
Skin areas that appear red, inflamed, or scaly and do not improve with time may indicate the presence of cancerous cells.
Spots or growths that are shiny or waxy
Any spot or growth on the skin that has a shiny, pearly, or waxy appearance should be examined by a dermatologist.
This image is property of www.skincarenetwork.co.uk.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma often presents with distinct features that can help differentiate it from other types of skin cancer. Look out for the following signs:
Raised and pearly appearance
BCC typically appears as a raised bump with a pearly or waxy texture. The skin surrounding the bump may have a translucent quality.
Small, red, or pink bumps
Small, red, or pink bumps that may become fragile and bleed easily can also indicate basal cell carcinoma.
Pink growths with raised edges and a central indentation
Pink growths that have raised, rolled edges and a central indentation are classic signs of BCC.
Open sores that ooze or crust
BCC can also appear as open sores that fail to heal, ooze, or form a crust.
Shiny, translucent, or waxy bumps
Bumps that appear shiny, translucent, or waxy can be indicative of basal cell carcinoma.
Scar-like white or yellow area without a defined border
A scar-like white or yellow area on the skin, which lacks a well-defined border, may also be a sign of BCC.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma manifests differently from basal cell carcinoma. Pay attention to the following signs:
Persistent red patches
SCC may present as rough, scaly, or crusted flat patches of skin that are red or inflamed.
Rough or scaly skin
Chronically rough or scaly patches of skin, especially if they are repeatedly irritated or bleed, should be evaluated.
Crusty or wart-like growths
Squamous cell carcinoma can also appear as crusted, wart-like growths on the skin.
Open sores that don’t heal
Non-healing sores or ulcers can be a sign of SCC and require medical attention.
Raised and firm nodules
SCC can manifest as raised nodules on the skin that feel firm to the touch.
Bleeding or ulcerated growths
Growths that bleed easily or ulcerate can be indicative of squamous cell carcinoma and should be examined promptly.
This image is property of images.everydayhealth.com.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most aggressive form of skin cancer, which can appear differently from other skin growths. Watch for the following signs:
Moles with an irregular or asymmetrical shape
Melanoma often exhibits irregular or asymmetrical shapes, unlike benign moles that are typically round or oval.
Moles with uneven or jagged borders
Moles that have borders that are uneven, ragged, or notched should be closely monitored.
Moles with varying colors or shades
Melanoma may have different colors or shades within the mole, such as brown, black, white, red, or blue.
Moles with a diameter larger than a pencil eraser
If a mole is larger than the size of a pencil eraser, it should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
Moles that evolve or change in size, shape, or color
Any mole that evolves or changes over time in terms of size, shape, or color should be examined.
Itchiness or tenderness in moles
Melanoma may cause moles to become itchy, tender, or painful, which should be assessed by a healthcare professional.
Bleeding or oozing of moles
Any mole that bleeds, oozes, or exhibits a crust should be promptly evaluated by a dermatologist.
Less Common Types of Skin Cancer
While basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma are the most prevalent types of skin cancer, there are other less common forms to be aware of:
Kaposi sarcoma
Kaposi sarcoma is a type of skin cancer that typically presents as reddish or purple lesions on the skin. It is commonly associated with a weakened immune system.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer that usually appears as firm, painless nodules or tumors on the skin. It is commonly found on sun-exposed areas.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer that starts in the oil glands of the skin. It often presents as firm, painless nodules or masses and can resemble other skin conditions.
This image is property of www.oakleafsurgical.com.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any suspicious or concerning changes to your skin, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Remember, early detection and intervention are vital for successful treatment. Here are some circumstances that warrant a visit to a healthcare professional:
Any suspicious or concerning skin changes
If you have any skin changes that are out of the ordinary or concerning, such as new growths, changes in existing moles, or persistent sores, it is wise to have them checked by a dermatologist.
Changes that are different from your usual moles or skin spots
If you notice changes in your moles or skin spots that are different from what you have previously observed, it is important to have them evaluated.
Rapidly growing or changing moles
Moles that are rapidly growing, changing in shape, color, or size, or exhibiting other irregularities should be assessed by a healthcare professional.
Symptoms that persist or worsen over time
If you experience symptoms such as itchiness, tenderness, bleeding, or oozing in relation to your skin spots or growths, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
Highly irregular or atypical moles
If you have moles that are highly irregular, atypical in appearance, or exhibit several warning signs discussed earlier, it is crucial to consult with a dermatologist.
Persistent skin sores that don’t heal
Non-healing sores or ulcers on the skin that persist should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
In conclusion, skin cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and intervention. By familiarizing yourself with the types of skin cancer, risk factors, prevention methods, and early signs to look out for, you can take proactive steps towards protecting your skin health. Remember, if you notice any concerning changes or symptoms, do not hesitate to seek medical attention. Your health and well-being are worth it!