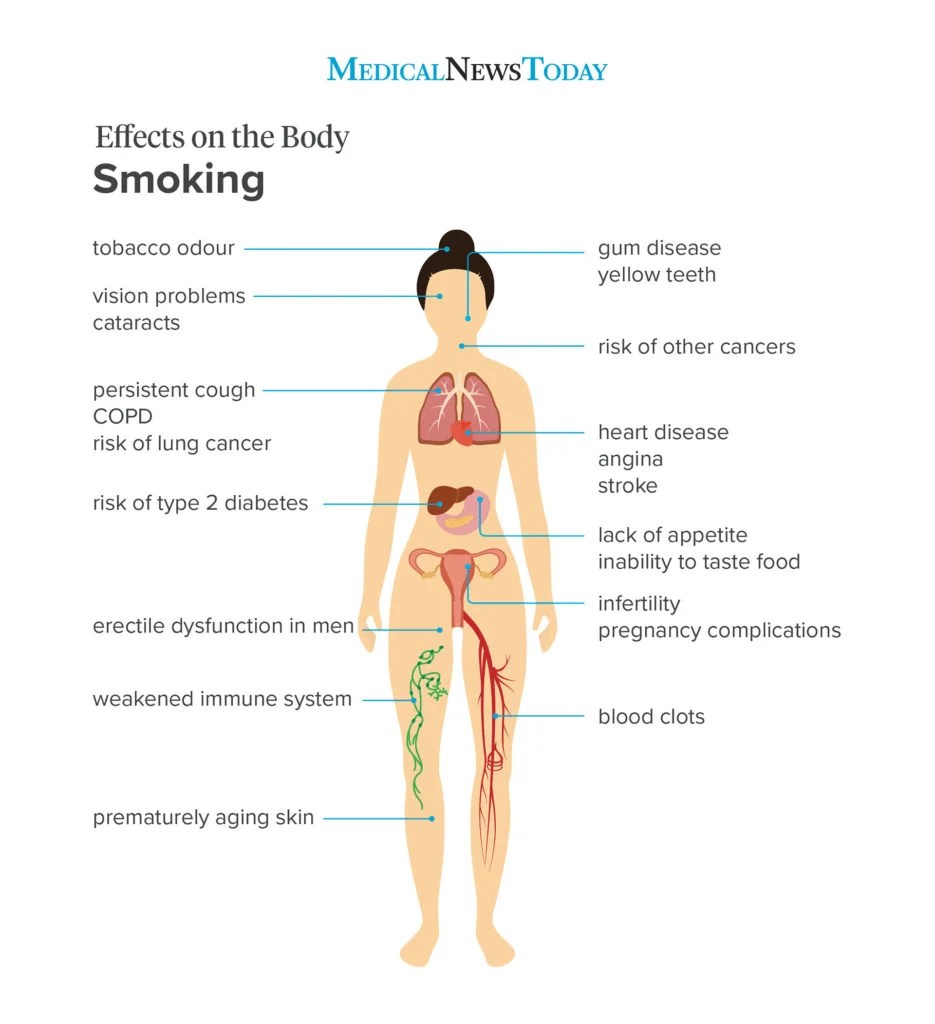
Smoking has a profound impact on your health, but have you ever wondered just how it affects you? From increasing your risk of life-threatening diseases to damaging your respiratory system and skin, smoking takes a toll on various aspects of your well-being. In this article, we will explore the detrimental effects smoking has on your health, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the risks associated with this harmful habit. So, grab a seat, relax, and let’s uncover the truth about smoking and its impact on your overall health.
Cardiovascular System
Increased Heart Rate
When you smoke, the nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes cause your heart rate to increase. This is because these substances stimulate the production of adrenaline in your body. Adrenaline is a hormone that can increase the heart rate and constrict your blood vessels, leading to an increased workload for your heart. Over time, this increased heart rate can put strain on your cardiovascular system and increase the risk of heart problems.
High Blood Pressure
Smoking is a major contributor to high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the lining of your blood vessels, causing them to narrow and become less elastic. This makes it harder for blood to flow through your vessels, leading to an increase in blood pressure. High blood pressure puts extra stress on your heart and can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
Reduced Oxygen Supply
When you smoke, the harmful chemicals in cigarettes, such as carbon monoxide, can interfere with the oxygen-carrying capacity of your blood. These substances bind to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells, preventing them from effectively carrying oxygen to your body tissues. As a result, your body may not receive an adequate supply of oxygen, which can have detrimental effects on your overall health and wellbeing.
Coronary Artery Disease
Smoking is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which plaque builds up inside the arteries that supply blood to the heart. The chemicals in cigarettes can cause damage to the inner walls of the arteries, leading to the formation of fatty deposits. As these deposits accumulate, they can narrow or block the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. This can result in chest pain, shortness of breath, heart attacks, and even death.
Increased Risk of Heart Attack
Smoking greatly increases your risk of experiencing a heart attack. The chemicals in cigarettes can cause the plaque buildup in your arteries to rupture, forming blood clots. These blood clots can block the blood flow to your heart, leading to a heart attack. In fact, smokers are twice as likely to have a heart attack compared to non-smokers. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to reduce your risk of heart attack and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
Respiratory System
Lung Irritation
Smoking can cause irritation to your lungs, leading to inflammation and coughing. The chemicals in cigarettes irritate the airways, causing them to become inflamed and produce excess mucus. This can result in a persistent cough, chest discomfort, and wheezing.
Chronic Cough
A chronic cough is a common symptom experienced by smokers. Smoking irritates the lining of the airways and causes them to produce excess mucus. This can lead to a persistent cough that lasts for months or even years. Chronic coughing can be bothersome and affect your daily life.
Shortness of Breath
Smoking can cause shortness of breath, especially during physical activity. The chemicals in cigarettes damage the air sacs in your lungs, reducing their ability to expand and contract properly. This can make it more difficult for you to take deep breaths and get enough oxygen during exercise or other activities. Shortness of breath can significantly impact your quality of life and limit your ability to engage in physical activities.
Decreased Lung Function
Smoking can lead to decreased lung function over time. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes damage the structure and function of your lungs, making it harder for you to breathe in and exhale air. This can result in a decrease in lung capacity and an overall reduction in your ability to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from your body. Decreased lung function can have a negative impact on your energy levels, exercise tolerance, and overall health.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Smoking is the leading cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is a progressive lung disease that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Smoking damages the airways and air sacs in your lungs, leading to breathing difficulties, coughing, wheezing, and an increased risk of respiratory infections. COPD is a long-term, irreversible condition that can significantly impair your lung function and quality of life.
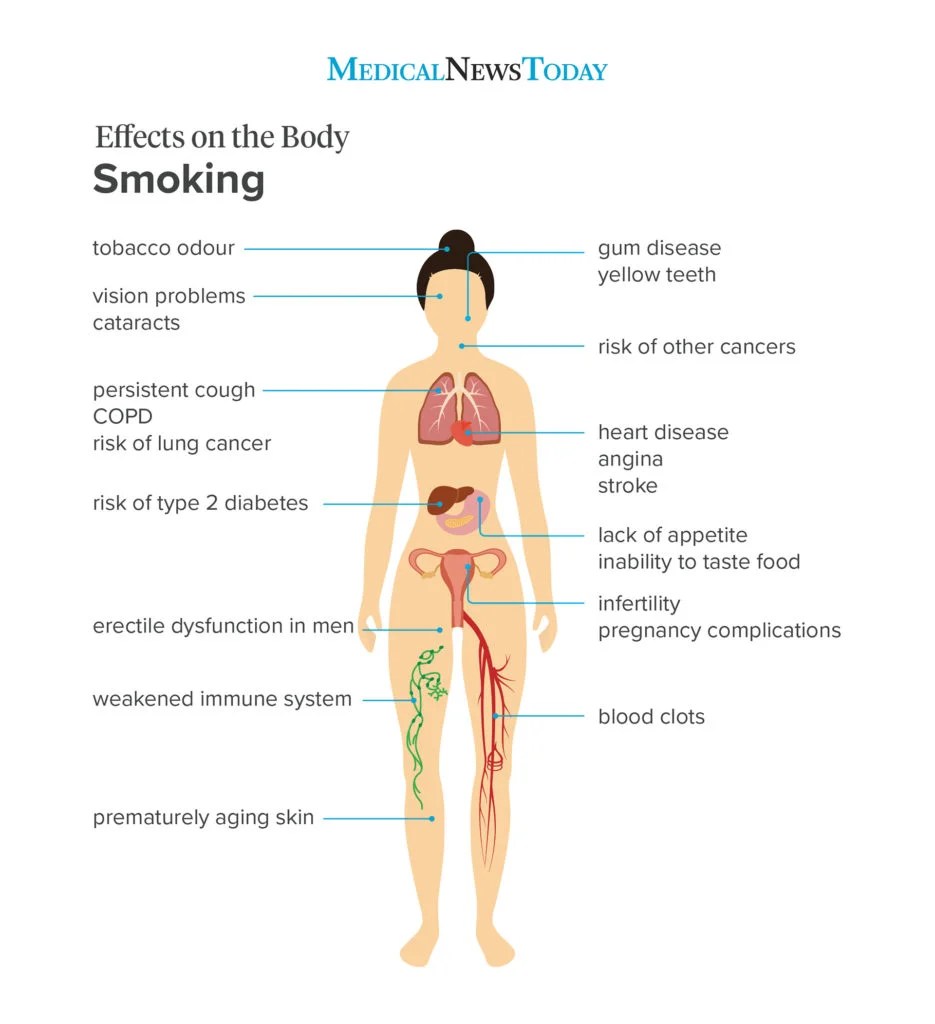
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Cancer
Lung Cancer
Smoking is the primary cause of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of all cases. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the DNA in your lung cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of tumors. Lung cancer often goes undetected in its early stages and can spread to other parts of the body. It is a deadly disease that is largely preventable by avoiding smoking or quitting if you are already a smoker.
Mouth Cancer
Smoking greatly increases the risk of developing various types of mouth cancer, including cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, and throat. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage the cells in your mouth, leading to the formation of malignant tumors. Mouth cancer can be disfiguring and have a significant impact on your ability to speak, eat, and swallow.
Throat Cancer
Smoking is a major risk factor for throat cancer, also known as laryngeal cancer. The chemicals in cigarettes can cause damage to the cells in your throat, leading to the formation of cancerous tumors. Throat cancer can affect your ability to speak, breathe, and swallow, and can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early.
Esophageal Cancer
Smoking increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer, which affects the tube that connects your throat to your stomach. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the lining of the esophagus, leading to the formation of cancerous cells. Esophageal cancer can cause difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and weight loss. It is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Bladder Cancer
Smoking is a significant risk factor for bladder cancer. The chemicals in cigarettes are excreted in your urine and can come into contact with the lining of your bladder. This can lead to DNA damage and the formation of cancerous cells. Bladder cancer can cause blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain during urination. It is important to seek medical advice if you experience any of these symptoms.
Fertility and Pregnancy
Reduced Fertility
Smoking can have a negative impact on fertility in both men and women. In women, smoking can affect the quality of eggs and interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. In men, smoking can reduce sperm count, motility, and morphology. It can also increase the risk of erectile dysfunction. If you are trying to conceive, quitting smoking is important to maximize your chances of success.
Increased Risk of Miscarriage
Smoking during pregnancy significantly increases the risk of miscarriage. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can restrict blood flow to the placenta, reducing the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus. This can lead to complications and an increased risk of miscarriage. Quitting smoking before pregnancy or as early as possible during pregnancy is crucial for the health of both the mother and the baby.
Premature Birth
Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of premature birth, which is when the baby is born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Premature babies may experience a variety of health problems, including respiratory difficulties, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays. Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to reduce the risk of premature birth and improve the health outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Low Birth Weight
Babies born to mothers who smoke are more likely to have a low birth weight. This means that they weigh less than 5.5 pounds at birth. Low birth weight can increase the risk of various health problems for the baby, including respiratory difficulties, developmental delays, and even infant mortality. Quitting smoking is essential to promote healthy fetal growth and ensure a healthier start for your baby.
Stillbirth
Smoking during pregnancy can increase the risk of stillbirth, which is the loss of a baby before birth after 20 weeks of pregnancy. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can restrict blood flow to the uterus, leading to complications that can result in stillbirth. It is important to prioritize the health of both the mother and the baby by quitting smoking before or during pregnancy.
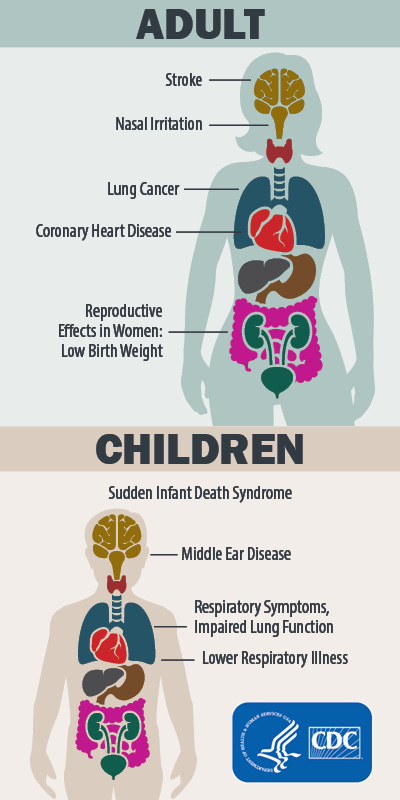
This image is property of www.cdc.gov.
Immune System
Weakened Immune Response
Smoking weakens your immune system and makes you more susceptible to infections. The chemicals in cigarettes can impair the function of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which play a crucial role in defending your body against harmful pathogens. As a result, smokers are more likely to develop infections and experience longer recovery times.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Smokers are more susceptible to infections, including respiratory infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage the cilia in your respiratory tract, which are responsible for clearing bacteria and other particles from your airways. This makes it easier for harmful pathogens to invade your body and cause infections.
Delayed Healing of Wounds
Smoking can delay the healing process of wounds and injuries. The chemicals in cigarettes can constrict your blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the injured area. This can impair the delivery of oxygen and nutrients needed for proper wound healing. The toxins in cigarettes can also negatively affect collagen production, which is essential for tissue repair.
Reduced Effectiveness of Vaccines
Smoking can reduce the effectiveness of vaccines. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can impair the immune response to vaccines, making them less effective in providing protection against diseases such as influenza and pneumonia. It is important to prioritize your health by quitting smoking and ensuring that you receive necessary vaccinations to protect yourself and those around you.
Risk of Autoimmune Diseases
Smoking increases the risk of developing autoimmune diseases, which occur when your immune system mistakenly attacks your own healthy cells and tissues. Smoking can trigger an immune response that leads to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. This can increase the risk of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. Quitting smoking is important to reduce the risk of developing these chronic and potentially debilitating conditions.
Oral Health
Tooth Discoloration
Smoking can cause tooth discoloration, giving your teeth a yellow or brownish appearance. The chemicals in cigarettes can stain the enamel on your teeth, making them look dull and discolored. This can have a negative impact on your smile and overall dental aesthetics.
Bad Breath
Smoking can cause bad breath, also known as halitosis. The chemicals in cigarettes can linger in your mouth and lungs, leading to an unpleasant odor in your breath. In addition, smoking can dry out your mouth, reducing the production of saliva, which plays a crucial role in washing away bacteria and keeping your mouth clean and fresh.
Gum Disease
Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can irritate your gums and cause inflammation. Over time, this can lead to gum recession, tooth loss, and even bone damage. Quitting smoking is essential to improve your gum health and reduce the risk of gum disease.
Tooth Loss
Smoking significantly increases the risk of tooth loss. The chemicals in cigarettes can weaken the structures that support your teeth, including the gum tissue and bone. This can result in loosening of the teeth and eventual tooth loss. Quitting smoking is crucial to protect your oral health and preserve your natural teeth.
Oral Cancer
Smoking greatly increases the risk of developing oral cancer, including cancers of the mouth, lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage the cells in your mouth and throat, leading to the formation of cancerous tumors. Oral cancer can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. It is important to prioritize your oral health and quit smoking to reduce your risk of developing this serious condition.
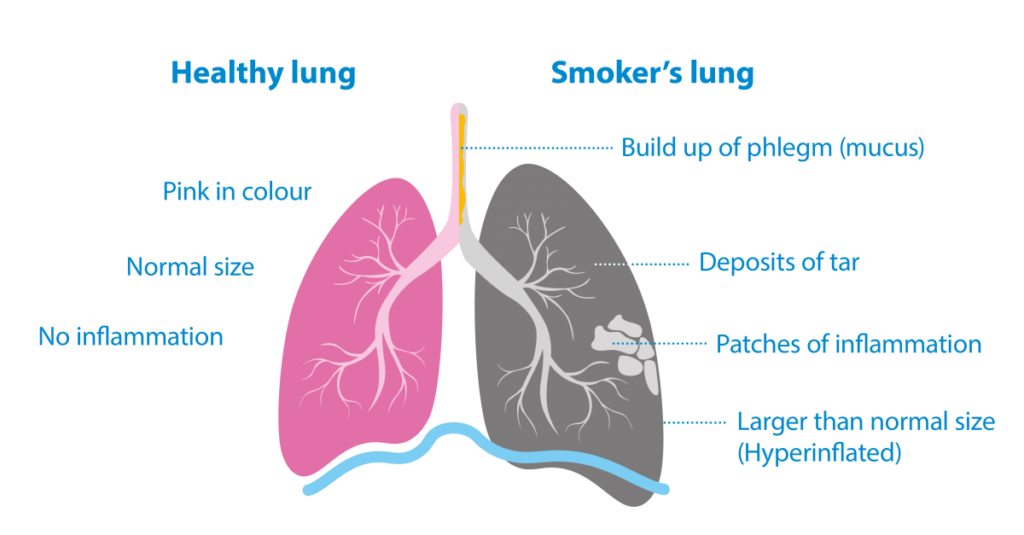
This image is property of www.asthmaandlung.org.uk.
Mental Health
Increased Risk of Depression
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing depression. The nicotine in cigarettes can have physiological and psychological effects that can contribute to the development of depressive symptoms. Smoking cessation has been shown to improve mental health outcomes and reduce the risk of depression.
Anxiety Disorders
Smokers are more likely to develop anxiety disorders compared to non-smokers. The nicotine in cigarettes can temporarily relieve anxiety symptoms, leading to a reliance on smoking as a coping mechanism. However, this relief is short-lived and can ultimately contribute to increased anxiety levels. Quitting smoking is crucial to break this cycle and improve your overall mental wellbeing.
Stress
Smoking is often used as a means to cope with stress. However, smoking can actually increase stress levels in the long run. The addictive nature of nicotine can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which can contribute to feelings of irritability and stress. Quitting smoking and finding healthier ways to manage stress, such as exercise or relaxation techniques, can lead to improved stress management and overall mental health.
Addiction
Smoking is highly addictive, and quitting smoking can be challenging. The nicotine in cigarettes activates the reward centers in your brain, leading to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. Over time, your body becomes dependent on nicotine, and quitting smoking can result in withdrawal symptoms such as cravings, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It is important to seek support and develop strategies to overcome nicotine addiction and achieve long-term cessation.
Impaired Cognitive Function
Smoking is associated with impaired cognitive function, such as memory loss and decreased attention span. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can negatively affect the blood flow to your brain, reducing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients needed for proper brain function. Quitting smoking can improve cognitive function and protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Digestive System
Nausea
Smoking can cause nausea, especially in new or occasional smokers. Nicotine, one of the main addictive substances in cigarettes, can irritate your stomach lining and cause feelings of queasiness. Nausea is often experienced by individuals who smoke on an empty stomach or smoke excessively.
Decreased Appetite
Smoking can suppress your appetite and lead to decreased food intake. Nicotine acts as an appetite suppressant and can reduce cravings for food. This can have negative effects on your nutritional status and overall health. It is important to prioritize a healthy diet and quit smoking to improve your appetite and ensure you are getting adequate nutrition.
Stomach Ulcers
Smoking is a significant risk factor for stomach ulcers, also known as peptic ulcers. The chemicals in cigarettes can weaken the protective lining of your stomach, making it more susceptible to damage from stomach acid. This can result in the development of painful sores in the lining of your stomach or small intestine. Quitting smoking is important to reduce the risk of stomach ulcers and promote the healing of existing ulcers.
Gastric Cancer
Smoking increases the risk of developing gastric cancer, which is cancer of the stomach. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage the cells in your stomach lining, leading to the formation of cancerous tumors. Gastric cancer can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, unintentional weight loss, and gastrointestinal bleeding. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms and prioritize your health by quitting smoking.
Pancreatic Cancer
Smoking is a major risk factor for pancreatic cancer, a deadly form of cancer that affects the pancreas. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the DNA in your pancreatic cells, leading to the formation of cancerous tumors. Pancreatic cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage and has a poor prognosis. Quitting smoking is crucial to reduce your risk of developing this aggressive and difficult-to-treat cancer.
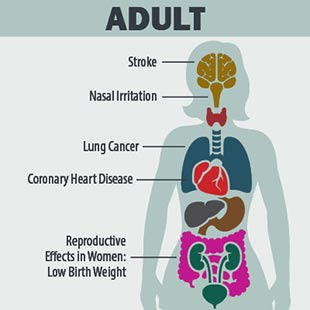
This image is property of www.cdc.gov.
Skin
Premature Aging
Smoking can cause premature aging of your skin. The chemicals in cigarettes can accelerate the breakdown of collagen and elastin, which are proteins that keep your skin firm and elastic. As a result, smoking can contribute to the development of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin. Quitting smoking can help slow down the aging process and improve the appearance of your skin.
Wrinkles
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing wrinkles. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the collagen and elastin fibers in your skin, leading to a loss of elasticity and the formation of wrinkles. Smoking can also reduce blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients and oxygen. Quitting smoking is important to protect your skin health and prevent the premature onset of wrinkles.
Dull Complexion
Smoking can contribute to a dull complexion. The chemicals in cigarettes can reduce blood flow to your skin, leading to a lack of nourishment and a decrease in the natural radiance of your skin. Smoking can also impair the production of new skin cells, resulting in a dull and lackluster appearance. Quitting smoking can improve your skin’s vitality and restore a healthy and vibrant complexion.
Grayish Skin Tone
Smoking can give your skin a grayish or yellowish tone. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can reduce the oxygen levels in your blood, leading to a lack of oxygen supply to your skin. This can result in a pale and unhealthy complexion. Quitting smoking can improve blood circulation and restore a healthier skin tone.
Increased Risk of Skin Cancer
Smoking increases the risk of developing skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the DNA in your skin cells, leading to the formation of cancerous tumors. Skin cancer can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. It is important to prioritize your skin health and quit smoking to reduce your risk of developing this serious condition.
Secondhand Smoke
Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections
Exposure to secondhand smoke can increase your risk of developing respiratory infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Secondhand smoke contains many of the same harmful chemicals as directly inhaled smoke, which can irritate the airways and impair immune function. Children, pregnant women, and individuals with preexisting respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable to the effects of secondhand smoke.
Asthma
Exposure to secondhand smoke can trigger asthma symptoms in individuals with the condition. Secondhand smoke irritates the airways and can cause inflammation and constriction of the bronchial tubes, leading to wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. It is important to create smoke-free environments to protect the respiratory health of those around you, especially individuals with asthma.
Ear Infections in Children
Children exposed to secondhand smoke are more likely to develop ear infections. The chemicals in secondhand smoke can irritate the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the throat, leading to fluid buildup and increased risk of infections. Ear infections can cause pain, temporary hearing loss, and even long-term complications if left untreated.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Smoking during pregnancy and exposing infants to secondhand smoke significantly increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). The chemicals in cigarettes can interfere with the normal development of a baby’s respiratory system, making them more susceptible to SIDS. It is crucial to create a smoke-free environment for babies to ensure their safety and reduce the risk of SIDS.
Lung Cancer in Non-Smokers
Exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of developing lung cancer in non-smokers. The chemicals in secondhand smoke can be inhaled by individuals who are in close proximity to smokers. This can lead to DNA damage and the formation of cancerous cells in their lungs. It is important to prioritize the health of those around you by quitting smoking and creating smoke-free environments.
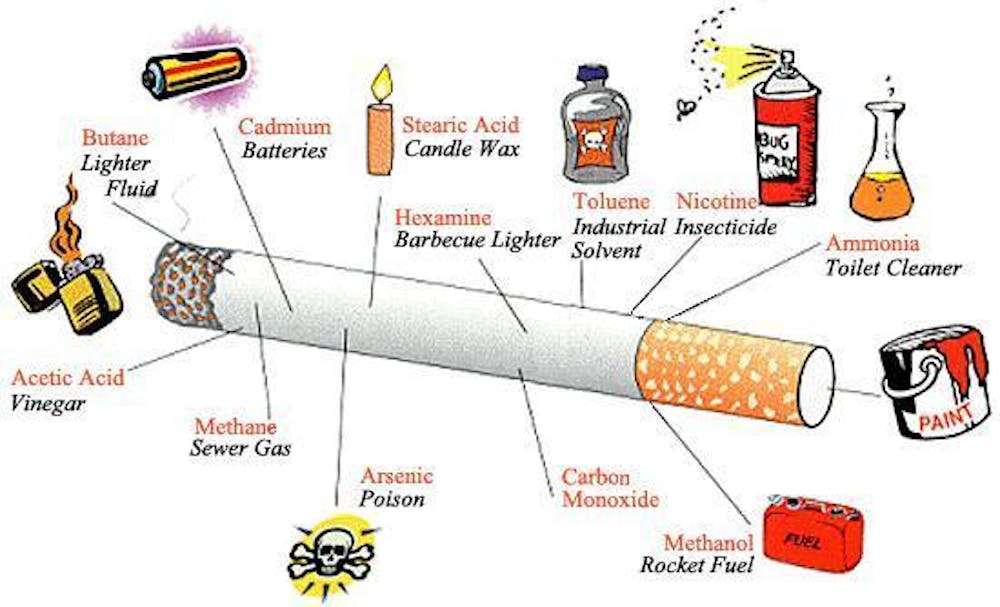
This image is property of images.theconversation.com.