
Menopause, a natural phase in a woman’s life, brings about various changes that can impact women’s health. From hormonal fluctuations to physical symptoms, the transition into menopause can be both challenging and transformative. Understanding how menopause affects women’s health is essential in order to navigate this new chapter with knowledge and confidence. In this article, we will explore the different ways menopause can impact various aspects of women’s overall well-being, from mental and emotional health to physical and sexual changes. So, let’s dive into the incredible journey of menopause and discover how it can shape a woman’s health.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Physical Effects of Menopause
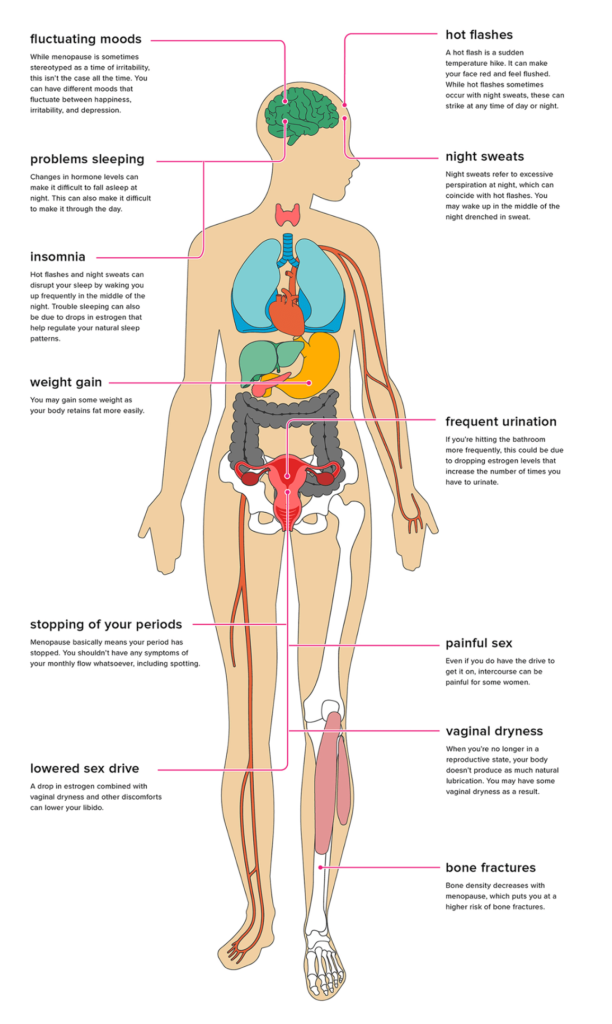
Hot flashes
Hot flashes are one of the most common symptoms experienced during menopause. They are characterized by sudden and intense feelings of heat, often accompanied by sweating and flushing of the skin. Hot flashes can occur both during the day and at night, and they can range from mild to severe. They can be disruptive to daily life, causing discomfort and interrupting sleep patterns.
Night sweats
Night sweats, also known as nocturnal hyperhidrosis, are similar to hot flashes but specifically occur during sleep. They can be extremely bothersome, causing women to wake up drenched in sweat and needing to change their nightwear and bedding. Night sweats can lead to poor sleep quality and fatigue, impacting a woman’s overall well-being.
Vaginal dryness
Vaginal dryness is a common physical effect of menopause that can cause discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse. The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause can result in a decrease in vaginal lubrication, leading to dryness, itching, and irritation. This can affect sexual relationships, causing discomfort and a decline in sexual desire.
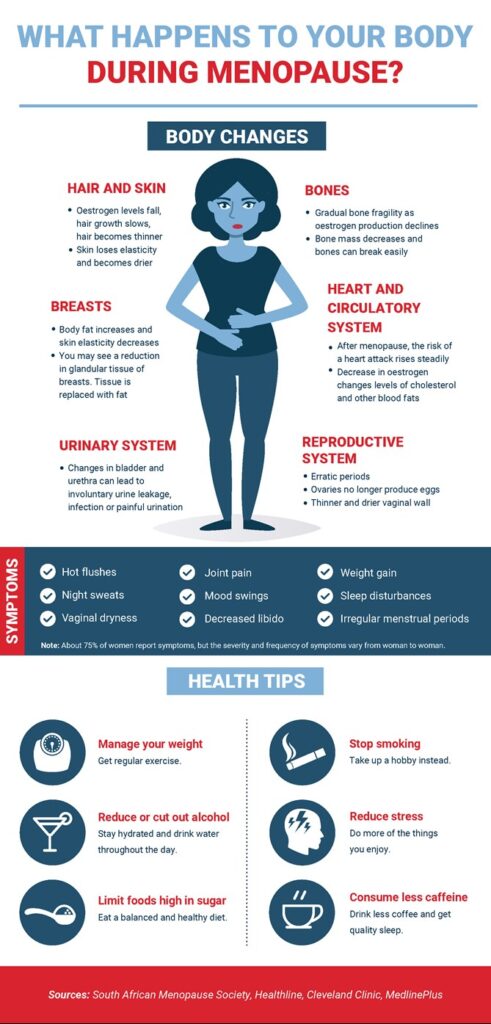
Loss of bone density
Menopause is associated with a decline in bone density, which can put women at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis. As estrogen levels decrease, bone resorption (breakdown) exceeds bone formation, leading to a gradual loss of bone density. This can result in brittle bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Weight gain
Weight gain is a common concern for many women going through menopause. The hormonal changes that occur during this stage of life can lead to a redistribution of fat, with a tendency for more weight to be stored around the abdomen. Additionally, a decrease in muscle mass and a slower metabolism can contribute to weight gain. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can help mitigate these effects.
Changes in cholesterol levels
Menopause can have an impact on cholesterol levels in women. The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to changes in the levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and HDL (good) cholesterol in the body. These changes can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle are important for overall health.
Hair thinning and loss
Many women experience changes in their hair during menopause, including hair thinning and loss. This can be attributed to a decrease in estrogen levels, which can affect hair follicles and lead to a reduction in hair volume. While not all women experience significant hair loss, it can cause distress and impact self-esteem. Proper hair care and nourishment can help minimize the effects of hair changes during menopause.
Skin changes
The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause can also affect the skin. It can lead to a decrease in collagen production, which results in the loss of skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles. Additionally, the skin may become drier and more prone to itchiness and irritation. Protecting the skin from sun exposure and maintaining a good skincare routine can help mitigate these changes.
Joint and muscle pain
Many women experience joint and muscle pain during menopause. The decrease in estrogen levels can contribute to inflammation and stiffness in the joints, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility. Muscle aches and pains can also occur, making daily activities more challenging. Regular exercise, stretching, and maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate joint and muscle pain.
Increased risk of chronic diseases
Menopause is associated with an increased risk of various chronic diseases, including heart disease, osteoporosis, and diabetes. The hormonal changes that occur during menopause can have a profound impact on the body, increasing susceptibility to these conditions. It is important for women to be proactive about their health during this stage of life, seeking regular medical check-ups and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
Emotional and Mental Effects of Menopause
Mood swings
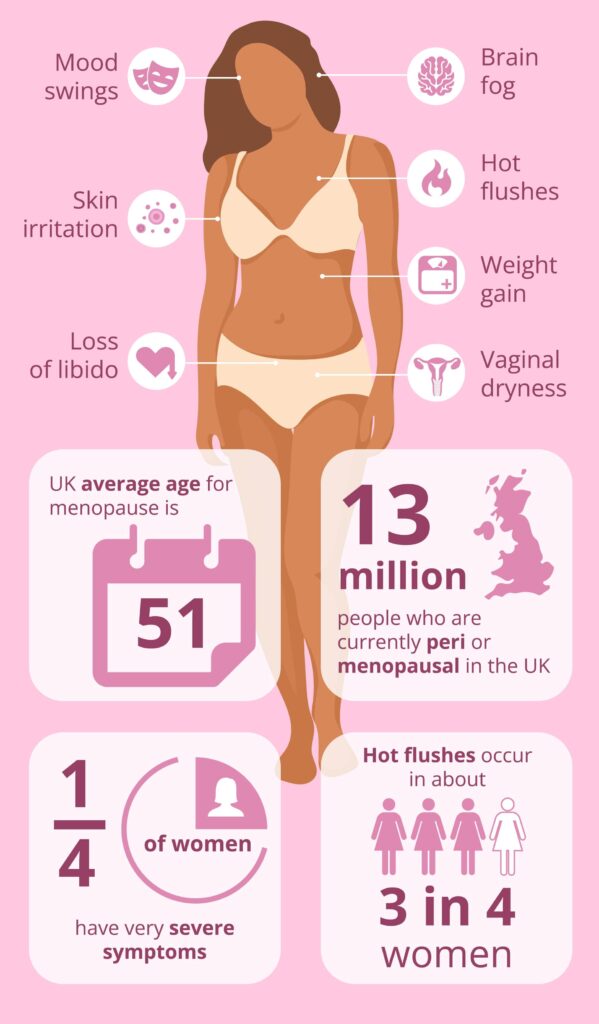
Mood swings are a common emotional symptom of menopause. Fluctuations in hormone levels can affect neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to changes in mood and emotional well-being. Women may experience heightened emotions, irritability, and feelings of sadness or anxiety. Support from loved ones, stress management techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage mood swings.
Depression and anxiety
Menopause can increase the risk of developing depression and anxiety. The hormonal changes during this stage of life can affect brain chemistry and contribute to the onset of these mental health conditions. Women may experience feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or worry. Seeking professional help and engaging in therapy or counseling can be beneficial in managing depression and anxiety symptoms.
Irritability
Irritability is a common emotional effect of menopause, often linked to hormonal fluctuations and disrupted sleep patterns. Women may find themselves becoming easily agitated or reacting more strongly to certain situations. Recognizing triggers and practicing relaxation techniques can help manage irritability and improve overall emotional well-being.
Difficulty concentrating
Many women report difficulty concentrating and experiencing “brain fog” during menopause. This can make it challenging to focus on tasks, remember information, and maintain mental clarity. Strategies such as creating a structured routine, breaking tasks into smaller chunks, and incorporating brain exercises can help improve concentration and cognitive function.
Memory problems
Memory problems can be a frustrating symptom of menopause. Women may find themselves forgetting appointments, struggling to recall names or details, and feeling like they have a “fuzzy” memory. Improving sleep quality, engaging in mental exercises, and practicing stress management techniques can support memory function during menopause.
Sleep disturbances
Sleep disturbances are common during menopause and can significantly impact overall well-being. Hormonal changes and physical symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and reduced daytime functioning. Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can improve sleep quality during menopause.
Reduced libido
Many women experience a decrease in sexual desire or libido during menopause. Hormonal changes, physical symptoms such as vaginal dryness, and emotional factors can contribute to a decline in sexual satisfaction. Open communication with partners, exploring new ways to enhance intimacy, and considering treatments such as hormone therapy or lubricants can help improve sexual well-being.
Decreased self-esteem
Menopause can affect a woman’s self-esteem, particularly due to physical changes such as weight gain, hair loss, and changes in body composition. Women may feel self-conscious or less confident in their appearance. Engaging in self-care activities, seeking support from loved ones, and focusing on positive aspects of oneself can help boost self-esteem during this transitional period.
Changes in body image
Menopause can bring about changes in body image, leading to feelings of insecurity or dissatisfaction with one’s physical appearance. It is important to remember that bodies change naturally over time, and it is essential to embrace self-acceptance and practice self-love. Engaging in activities that promote body positivity, such as exercising for pleasure and nourishing the body with healthy foods, can support a positive body image.
Impact on relationships
Menopause can have an impact on relationships, both intimate and familial. Physical symptoms, emotional changes, and a shift in priorities can affect communication and intimacy within relationships. Open and honest communication with partners and seeking support from loved ones can help navigate the changes and maintain strong and fulfilling relationships.
Cardiovascular Health and Menopause
Increased risk of heart disease
Menopause is associated with an increased risk of heart disease in women. Estrogen plays a protective role in maintaining heart health, and its decline during menopause can contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels are crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health during menopause.
Changes in blood pressure
Menopause can lead to changes in blood pressure. Fluctuations in hormone levels and the aging process can contribute to increased blood pressure. Monitoring blood pressure regularly and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can help manage blood pressure during menopause.
Effects on cholesterol levels
The hormonal changes during menopause can impact cholesterol levels, leading to unfavorable changes in LDL (bad) cholesterol and HDL (good) cholesterol. This can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions. Regular check-ups and adopting a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
Impact on blood vessels
Menopause can affect the health and function of blood vessels. Estrogen has a protective effect on the inner lining of blood vessels, promoting their elasticity and preventing the buildup of plaque. With its decline during menopause, blood vessels may become stiffer and more susceptible to damage. Eating a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding smoking are crucial for maintaining vascular health.
Link to stroke
Menopause is associated with an increased risk of stroke. The hormonal changes and age-related factors during this stage of life can contribute to the development of stroke. It is essential to manage other risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, and to seek medical advice if any stroke symptoms occur.
Importance of healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for promoting cardiovascular health during menopause. This includes engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, managing stress levels, getting enough sleep, and avoiding tobacco use. These lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be considered for women experiencing severe menopausal symptoms, including those affecting cardiovascular health. However, the decision to undergo HRT should be individualized and made in consultation with a healthcare provider. The risks and benefits of HRT should be carefully weighed, taking into account a woman’s overall health and medical history.
Sexual Health and Menopause
Vaginal dryness and discomfort
Vaginal dryness is a common symptom of menopause that can cause discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse. The decrease in estrogen levels reduces vaginal lubrication, leading to dryness and irritation. Using water-based lubricants or moisturizers can help alleviate symptoms and improve sexual comfort.
Decreased sexual desire
Many women experience a decrease in sexual desire or libido during menopause. Hormonal changes, physical symptoms, and emotional factors can contribute to this change. Open communication with partners, exploring new ways to enhance intimacy, and seeking professional advice if needed can help address decreased sexual desire.
Painful intercourse
Vaginal dryness and thinning of vaginal walls can lead to painful intercourse, also known as dyspareunia. The discomfort can affect sexual relationships and overall sexual satisfaction. Using lubricants, engaging in longer foreplay, and considering hormone therapy or other treatments for vaginal dryness can help alleviate pain during intercourse.
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence, the involuntary leakage of urine, can occur during menopause. The decrease in estrogen levels can weaken the muscles supporting the bladder, leading to urinary symptoms. Pelvic floor exercises, lifestyle modifications, and, in severe cases, medical interventions can help manage urinary incontinence.
Impact on sexual relationships
Menopause can have an impact on sexual relationships, both physically and emotionally. Open and honest communication with partners, seeking professional advice, and exploring different approaches to intimacy can help strengthen and maintain sexual relationships. Understanding that sexual satisfaction may change during menopause is crucial for a fulfilling and satisfying sexual experience.
Treatment options
There are various treatment options available to address the sexual health challenges of menopause. These include hormone therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), local estrogen therapy, vaginal lubricants and moisturizers, and pelvic floor exercises. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate treatment based on individual needs and medical history.

This image is property of onewomanhealth.com.
Bone Health and Menopause
Loss of bone density
Menopause is associated with a loss of bone density due to the decline in estrogen levels. This can lead to an increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Regular weight-bearing exercises, a calcium-rich diet, and incorporating vitamin D intake are essential for maintaining bone health during menopause.
Increased risk of osteoporosis
The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause increases the risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened and brittle bones. Women are at a higher risk of osteoporosis than men due to hormonal and age-related factors. It is crucial to discuss bone density testing and management strategies with a healthcare provider.
Fracture risk
Women going through menopause are at an increased risk of fractures, especially in the hips, spine, and wrists. Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more prone to fractures from minor falls or trauma. Preventive measures such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can reduce the risk of fractures.
Importance of calcium and vitamin D
Calcium and vitamin D are essential nutrients for maintaining bone health. Calcium helps build and maintain strong bones, while vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods are good sources of calcium, and exposure to sunlight provides the body with vitamin D.
Exercise and weight-bearing activities
Regular weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, dancing, and strength training, can help maintain and improve bone density during menopause. These exercises promote bone formation and strengthen the muscles supporting the bones. Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for overall bone health and reducing the risk of fractures.
Hormone therapy as a preventive measure
Hormone therapy, specifically estrogen therapy, may be considered as a preventive measure for osteoporosis in women at high risk. However, the decision to undergo hormone therapy should be individualized and made in consultation with a healthcare provider. The benefits and risks of hormone therapy should be carefully evaluated.
Cognitive Function and Menopause
Memory problems
Many women experience memory problems during menopause. Hormonal changes, sleep disturbances, and aging processes can contribute to difficulties with memory and cognitive function. Strategies such as maintaining a structured routine, minimizing distractions, and engaging in mental exercises can help support memory function.
Difficulty concentrating
Difficulty concentrating is a common cognitive symptom of menopause. Fluctuations in hormone levels and other menopausal symptoms can make it challenging to focus on tasks and maintain mental clarity. Creating a conducive environment, breaking tasks into smaller steps, and practicing mindfulness techniques can improve concentration and cognitive function.
Brain fog
Brain fog refers to a feeling of mental fuzziness or clouded thinking. Many women experience brain fog during menopause, leading to difficulties with memory, concentration, and decision-making. Engaging in regular physical exercise, managing stress levels, and adopting a healthy diet can help alleviate brain fog symptoms.
Possible link to dementia
While there is no direct causative link between menopause and dementia, hormonal changes during menopause may contribute to the development of age-related cognitive decline. It is important to maintain overall brain health by engaging in mentally stimulating activities, managing chronic conditions, and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
Strategies for maintaining cognitive function
Maintaining cognitive function during menopause involves incorporating various strategies into daily life. Engaging in mental exercises such as puzzles and memory games, staying intellectually stimulated, managing stress, and getting enough sleep are beneficial for supporting cognitive health during this transitional phase.
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact cognitive function during menopause. Adopting a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and brain-boosting nutrients can support brain health. Regular physical exercise, stress reduction techniques, and quality sleep are also important factors in maintaining cognitive function.
Mental exercises
Engaging in mental exercises can help maintain cognitive function during menopause. Activities such as reading, puzzles, crosswords, and learning new skills keep the brain active and challenged. Socializing and participating in stimulating conversations also contribute to mental sharpness and overall well-being.
This image is property of www.ckbhospital.com.
Breast Health and Menopause
Changes in breast tissue
Menopause can bring about changes in breast tissue. Hormonal fluctuations and decreased estrogen levels can lead to a loss of breast fullness and firmness. The breasts may also become more tender or sensitive. Regular breast self-exams and routine check-ups with a healthcare provider are important for monitoring breast health.
Increased breast cancer risk
The risk of breast cancer increases with age, and menopause is a significant factor in this increased risk. While not all women will develop breast cancer, it is crucial to be vigilant about breast health. Following recommended guidelines for mammograms, performing regular breast self-exams, and seeking medical attention if any changes are noticed are important steps in early detection.
Breast pain and tenderness
Many women experience breast pain or tenderness during menopause. Hormonal fluctuations, as well as other factors such as fibrocystic breast changes, can contribute to these symptoms. Wearing a supportive bra, avoiding caffeine and other triggers, and applying warm or cold compresses can help alleviate breast pain and tenderness.
Importance of regular breast exams
Regular breast exams, including clinical exams and mammograms, are crucial for maintaining breast health during menopause. Clinical exams performed by a healthcare provider and mammograms are important tools for detecting any abnormalities or changes that may indicate breast cancer. Early detection greatly improves the chances of successful treatment.
Mammograms and screenings
Mammograms are X-ray images of the breasts used to detect early signs of breast cancer. Following recommended guidelines for mammogram screenings is important for women during menopause. The frequency and timing of mammograms may vary based on individual risk factors and healthcare provider recommendations.
Breast self-exams
Performing regular breast self-exams is an essential part of breast health during menopause. Women should be familiar with the normal look and feel of their breasts and report any changes or abnormalities to a healthcare provider. Breast self-exams can be done monthly and involve visually inspecting the breasts and feeling for any lumps or changes in texture.
Metabolic Health and Menopause
Weight gain and metabolism
Weight gain and changes in metabolism are common during menopause. Hormonal changes, aging, and shifts in body composition can lead to increased fat storage, particularly around the abdomen. This can contribute to an increased risk of metabolic conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity are important for metabolic health.
Changes in body composition
Menopause can lead to changes in body composition, including an increase in overall body fat and a decrease in lean muscle mass. These changes can affect metabolism and increase the risk of metabolic conditions. Resistance training exercises, along with maintaining a healthy diet rich in protein, can help preserve muscle mass and support overall body composition.
Impact on insulin resistance and blood sugar control
Menopause is associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance, a condition where cells have difficulty using insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This can contribute to the development of diabetes. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of metabolic conditions.
Increased risk of diabetes
The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause can increase the risk of developing diabetes. Estrogen plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. With its decline, insulin resistance may occur, leading to impaired blood sugar control. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical advice are important for diabetes prevention and management.
Diet and exercise strategies
Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity are key strategies for metabolic health during menopause. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables, along with regular aerobic exercise and strength training, can help manage weight, insulin sensitivity, and blood sugar control.
Monitoring blood glucose levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is important for women at risk of or living with diabetes during menopause. Regular monitoring can help identify any increases in blood sugar levels and guide appropriate management strategies. Lifestyle modifications, medication, and close medical supervision are essential components of diabetes care during menopause.
Importance of regular check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for maintaining metabolic health during menopause. Routine screenings, such as blood sugar tests, cholesterol checks, and blood pressure monitoring, can help identify any abnormalities or changes that may require intervention. Seeking medical advice and following recommended guidelines promote overall health and well-being.
This image is property of onlinedoctor.lloydspharmacy.com.
Gastrointestinal Health and Menopause
Digestive problems
Menopause can bring about digestive problems for some women. The hormonal changes during this stage of life can affect the function of the digestive system, leading to symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, and abdominal discomfort. Eating a balanced diet, managing stress levels, and staying hydrated can help alleviate digestive symptoms during menopause.
Changes in bowel movements
Changes in bowel movements can occur during menopause. Some women may experience constipation, while others may have looser stools or increased frequency. These changes can be attributed to hormonal fluctuations and alterations in the gut microbiome. A diet rich in fiber, regular physical activity, and staying hydrated can help regulate bowel movements.
Bloating and gas
Bloating and gas are common digestive symptoms during menopause. Hormonal changes can affect gastrointestinal motility and digestion, leading to increased gas production and abdominal discomfort. Eating smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding gas-producing foods, and managing stress levels can help minimize bloating and gas.
Increased risk of constipation
Menopause can increase the risk of constipation in some women. Hormonal changes, decreased physical activity, and dietary factors can contribute to sluggish bowel movements. Eating a fiber-rich diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity can help prevent and alleviate constipation.
Importance of fiber in the diet
Incorporating an adequate amount of fiber in the diet is essential for gastrointestinal health during menopause. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts are good sources of dietary fiber.
Fluid intake and hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining gastrointestinal health and overall well-being during menopause. Drinking enough fluids can help prevent constipation, support digestion, and alleviate bloating and gas. Aim for adequate water intake throughout the day and consider hydrating foods such as soups, fruits, and vegetables.
Regular physical activity
Regular physical activity is beneficial for gastrointestinal health during menopause. Exercise stimulates bowel movements and promotes regular digestion. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, or yoga can help regulate bowel movements and relieve digestive symptoms.
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of menopause on women’s health is crucial for navigating this transitional period. The physical effects of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and changes in bone density, can be managed through various lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Emotional and mental effects, including mood swings, depression, and difficulty concentrating, can be addressed through self-care practices, communication, and professional support. Prioritizing cardiovascular health, sexual health, bone health, cognitive function, breast health, metabolic health, and gastrointestinal health is essential during menopause. Seeking medical advice, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular check-ups are key steps in promoting overall well-being during this transformative stage of life. By being proactive and informed, women can navigate menopause with confidence and continue to thrive.

This image is property of balancemyhormones.co.uk.