
You’re probably familiar with the term “probiotics,” but do you know how they actually help in maintaining gut health? In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of probiotics and their role in keeping your gut in top shape. From improving digestion to boosting your immune system, probiotics are tiny superheroes that can make a big difference in your overall well-being. So, let’s dive into the wonderful world of probiotics and discover how these friendly bacteria work their magic in maintaining gut health!

This image is property of lirp.cdn-website.com.
Overview of Gut Health
Introduction to gut health
Gut health refers to the overall well-being and functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. It plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and positively impacts various bodily functions. A healthy gut is crucial for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, immune system strength, and mental well-being.
Importance of gut health
Maintaining optimal gut health is essential for several reasons. Firstly, the gastrointestinal tract is responsible for a significant portion of our immune system, with about 70% of immune cells residing in the gut. A healthy gut helps defend against harmful pathogens and bacteria, reducing the risk of infections and diseases.
Secondly, the gut is a key player in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. When the gut is functioning properly, it breaks down food efficiently and absorbs essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients necessary for overall health and vitality.
Lastly, a balanced gut contributes to mental well-being. Emerging research suggests a strong connection between the gut and the brain, also known as the gut-brain axis. A healthy gut microbiome (the community of microorganisms that resides in the gastrointestinal tract) helps regulate mood, cognition, and behavior, potentially reducing the risk of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Introduction to Probiotics
Definition of probiotics
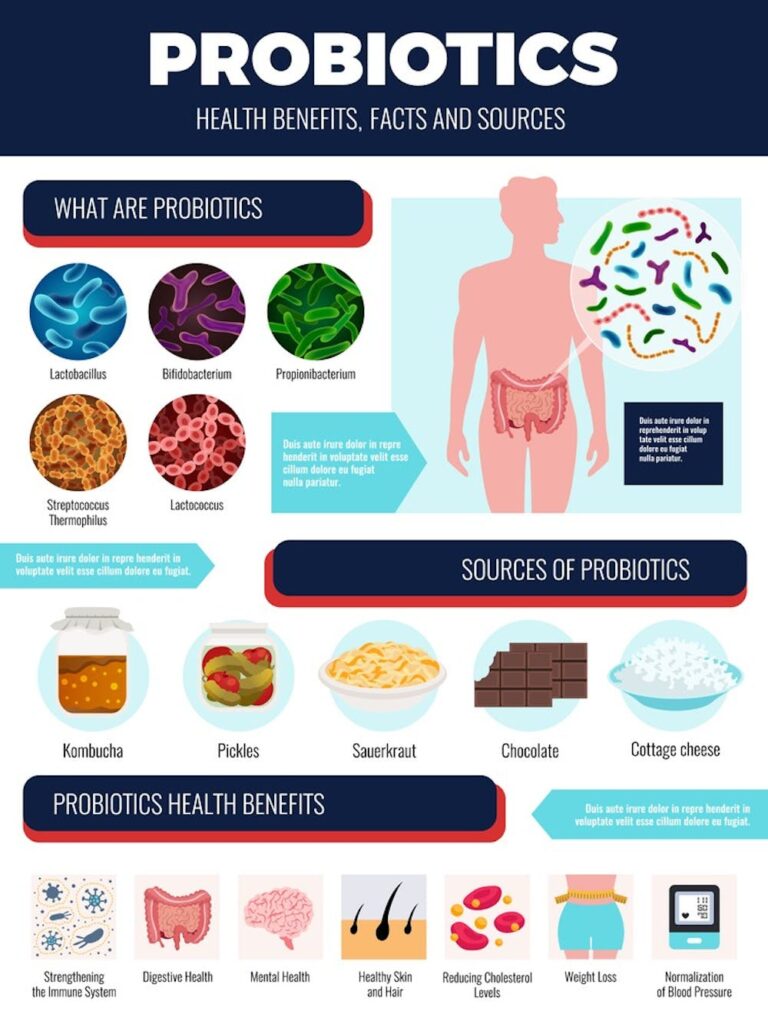
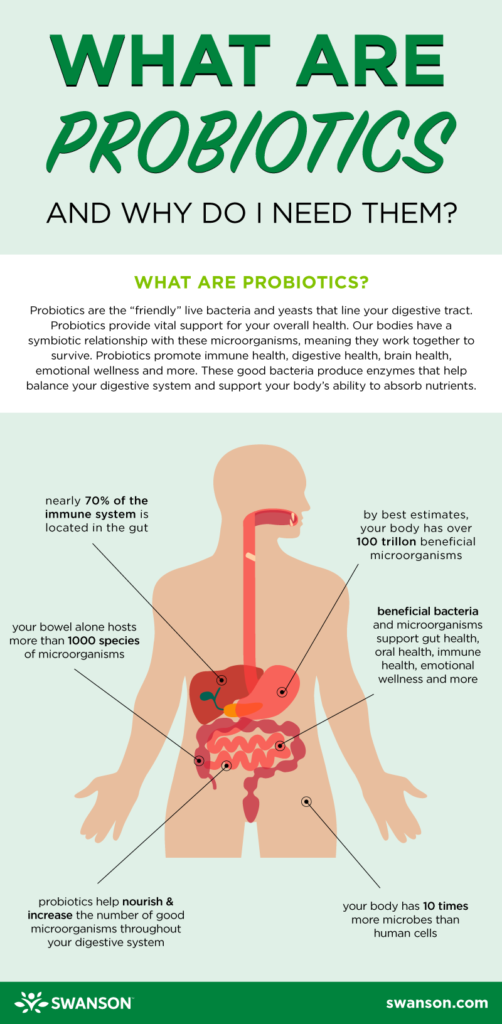
Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They are often referred to as “friendly bacteria” and are naturally present in the gut microbiome. These beneficial bacteria support proper digestion, immune health, and overall gut balance.
Types of probiotics
Probiotics can belong to different strains and species, each with unique properties and potential health benefits. Some commonly known probiotic strains include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Each strain may have specific effects on the body and can target different aspects of gut health.
Sources of probiotics
Probiotics can be obtained from various sources. Dairy products, such as yogurt and kefir, are rich in probiotics. Fermented foods, including sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso, also contain beneficial bacteria. Additionally, probiotic supplements are available in the form of capsules, powders, or liquids, offering a convenient way to incorporate probiotics into our diet.
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
Definition of gut microbiome
The gut microbiome refers to the billions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other tiny organisms, that reside in our gastrointestinal tract. These microorganisms play a pivotal role in maintaining overall gut health and are essential for various bodily functions.
Importance of a balanced gut microbiome
A balanced gut microbiome is essential for optimal health. When the microbiome is in harmony, beneficial bacteria dominate and help keep harmful bacteria in check. This balance promotes a healthy gut environment, supports optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, and contributes to a strong immune system.
Factors influencing the gut microbiome
Several factors can influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome. These include diet, lifestyle, stress levels, antibiotic use, and environmental factors. A poor diet high in processed foods and low in fiber can negatively impact the gut microbiome, leading to an imbalance known as dysbiosis. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods can promote a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
Mechanisms of Action
Restoring balance in the gut
Probiotics work by restoring the balance of the gut microbiome. When consumed, they can help increase the population of beneficial bacteria, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. This rebalancing effect can alleviate symptoms of gut dysbiosis and promote overall gut health.
Enhancing digestion and nutrient absorption
Certain strains of probiotics have been found to enhance digestion and nutrient absorption. For example, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis help break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, improving the overall efficiency of digestion and nutrient uptake.
Promoting intestinal barrier function
An intact intestinal barrier is crucial for preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. Probiotic bacteria strengthen the intestinal barrier by promoting the production of tight junction proteins, which seal the gaps between intestinal cells. This can help prevent the leakage of toxins and undigested food particles into the bloodstream.
Strengthening the immune system
Probiotics play a vital role in maintaining a robust immune system. They interact with immune cells located in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue, promoting their proper functioning. By activating immune cells and modulating immune responses, probiotics help defend against pathogens and reduce the risk of infections.
Reducing inflammation in the gut
Inflammation in the gut can lead to various digestive disorders and negatively impact overall health. Probiotics have been shown to modulate the immune response, reducing inflammation and promoting a healthy gut environment. This anti-inflammatory effect can alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).

This image is property of www.netmeds.com.
Specific Health Benefits of Probiotics
Alleviating gastrointestinal disorders
Probiotics have been extensively studied for their potential in alleviating gastrointestinal disorders such as IBS, IBD, and gastroenteritis. They can help reduce symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea, improving overall gut function and quality of life.
Preventing and treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea
Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of the gut microbiome, leading to antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Probiotics, especially strains of Lactobacillus and Saccharomyces boulardii, have shown promise in preventing and treating this common side effect of antibiotic therapy.
Supporting mental health and cognitive function
The gut-brain axis links the gut microbiome with mental health and cognitive function. Probiotics have been studied for their potential to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. By modulating neurotransmitter production and reducing inflammation, they may positively impact mental well-being.
Boosting the immune system
Probiotics can enhance immune function by stimulating the production of immune cells and promoting their proper functioning. This immune-boosting effect may help reduce the risk of respiratory infections, such as the common cold, and support overall immune health.
Enhancing skin health
Emerging research suggests a link between the gut microbiome and skin health. Probiotics have shown promise in improving various skin conditions, including acne, eczema, and rosacea. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, they may positively influence skin health and appearance.
Choosing the Right Probiotics
Identifying strains for specific health concerns
Different probiotic strains have different effects on the body, so it is important to choose the right strains for specific health concerns. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify the most appropriate probiotic strains based on individual needs and health conditions.
Considerations for selecting probiotic supplements
When selecting probiotic supplements, several factors should be considered. These include the number of live bacteria (CFUs) in each dose, the presence of multiple strains, and the viability and stability of the strains during shelf life. Look for products that have been third-party tested and meet quality standards to ensure their effectiveness.
Natural food sources of probiotics
In addition to supplements, probiotics can be obtained from natural food sources. Incorporating fermented foods into the diet, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, can provide a natural source of probiotics, along with other beneficial nutrients.
This image is property of snworksceo.imgix.net.
Probiotics and Digestive Disorders
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a common digestive disorder characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel movements. Probiotics, especially the strains Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus plantarum, have shown promising results in reducing IBS symptoms and improving overall gut function.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
IBD, which includes conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. Probiotics, particularly specific strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce disease activity in individuals with IBD.
Constipation and diarrhea
Probiotics can help regulate bowel movements and alleviate symptoms of constipation and diarrhea. Certain strains, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium lactis, have been shown to improve stool frequency, consistency, and overall digestive comfort.
Probiotics for Immune Support
Preventing respiratory infections
Respiratory infections, such as the common cold and flu, are a common occurrence, especially during colder months. Probiotics, when taken regularly, can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Reducing the risk of urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are often caused by harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli. Probiotics, particularly strains of Lactobacillus, can help prevent UTIs by promoting a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract and inhibiting the growth of pathogens.
Enhancing vaccine response
Probiotics have been shown to enhance the body’s immune response to vaccines. By stimulating the production of immune cells and modulating immune signaling pathways, probiotics can improve vaccine effectiveness, providing better protection against infectious diseases.
This image is property of www.swansonvitamins.com.
Safety and Side Effects
Common side effects of probiotics
Probiotics are generally safe for most individuals when taken as recommended. However, some people may experience minor side effects, such as gas, bloating, and mild digestive discomfort. These side effects are usually temporary and subside as the body adjusts to the probiotics.
Precautions for vulnerable populations
Certain populations, such as infants, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and individuals with compromised immune systems, should exercise caution when considering probiotic use. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting probiotic supplementation in these cases.
Interactions with medication
Some medications, such as antibiotics and immunosuppressants, can interact with probiotics. It is important to inform healthcare professionals about ongoing probiotic use to avoid potential interactions or conflicts with prescribed medications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining gut health is vital for overall well-being, and probiotics play a valuable role in achieving and maintaining optimal gut health. By restoring the balance of the gut microbiome, enhancing digestion and nutrient absorption, promoting intestinal barrier function, strengthening the immune system, and reducing inflammation, probiotics offer a range of health benefits. Incorporating probiotics into a healthy lifestyle, through natural food sources or supplements, can contribute to improved digestive function, enhanced immune support, and better overall health and well-being. As research in the field of probiotics continues to advance, further understanding of their mechanisms of action and specific health benefits will pave the way for future developments in gut health maintenance and support.

This image is property of www.nebraskamed.com.